Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Unsolved)
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Social Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions :
1. This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
2 All questions are compulsory.
3. Section-A: Question no, 1 to 5 are Very Short Answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
4. Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are Short Answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
5. Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are Long Answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
7. Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
(2 x 5 = 10)
1. Discuss the various stages of the Non-Cooperation Movement launched by Mahatma Gandhi.
2. The economic strength of a country lies in the development of manufacturing industries. Explain with the help of any two points.
3. Describe the necessity of political parties in a democratic country?
4. How can money be easily exchanged for goods or services? Give example to explain.
5. Read the data in the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
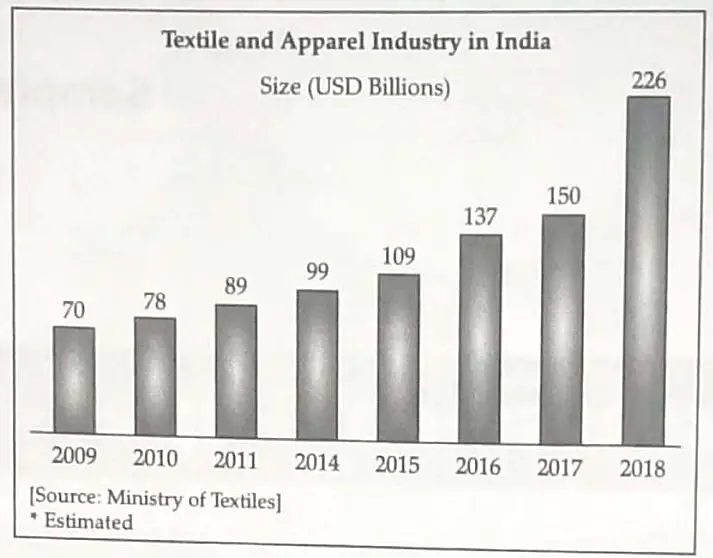
5.1 On the basis of the given data, give any one reason why the cotton textile industry has grown rapidly over the years in India.
5.2 Write any one factor which were responsible for the concentration of Cotton Textile Industry in Maharashtra and Gujarat in early years?
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions
(3 x 3 = 9)
6. Why did Gandhiji decide to withdraw the ‘Non-Cooperation Movement’ in February, 1922? Explain any three reasons.
7. What is meant by a ‘National Political Party’? State the conditions required to be a National Political Party.
8. “Poor households still depend on informal sources of credit”. Support the statement with examples.
OR
“Barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent in India since 1991.” Justify the statement.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions
(5 x 2 = 10)
9. Democracies do not appear to be very successful in reducing economic inequalities”. Justify the statement.
OR
What are the differences between democracy and dictatorship in the decision making process?
10. Why do multinational corporations (MNCS) set up their offices and factories in certain areas only? Explain any five reasons.
OR
Which type of deposits with the banks are called demand deposits? State some important features of demand deposits.
Section – D
Case Based Questions
(4 x 2 = 8)
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Emboldened with this success, Gandhiji in 1919 decided to launch a nationwide Satyagraha against the proposed Rowlatt Act (1919). This Act had been hurriedly passed through the Imperial Legislative Council despite the united opposition of the Indian members. It gave the government enormous powers to repress political activities, and allowed detention of political prisoners without trial for two years. Mahatma Gandhi wanted non-violent civil disobedience against such unjust laws, which would start with a strike on 6 April. Rallies were organised in various cities, workers went on strike in railway workshops, and shops closed down. Alarmed by the popular upsurge, and scared that lines of communication such as the railways and telegraph would be disrupted, the British administration decided to clamp down on nationalists. Local leaders were picked up from Amritsar, and Mahatma Gandhi was barred from entering Delhi. On 10 April, the police in Amritsar fired upon a peaceful procession, provoking widespread attacks on banks, post offices and railway stations. Martial law was imposed and General Dyer took command.
11.1 What was Rowlatt Act according to this paragraph? 1
11.2 What did Gandhiji do to protest against the Rowłatt Act? 1
11.3 What did Mahatma Gandhi actually want against laws such as Rowlatt Act? 2
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality. Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc., have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways.
The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life. It is thus, evident that a dense and efficient network of transport and communication is a prerequisite for local, national and global trade of today.
12.1 Why is there a need to interlink with the world? 1
12.2 Infer the importance of means of transportation and communication for socio-economic progress? 2
12.3. How does trade strengthen the economy of a country? 1
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
(1 x 3 = 3)
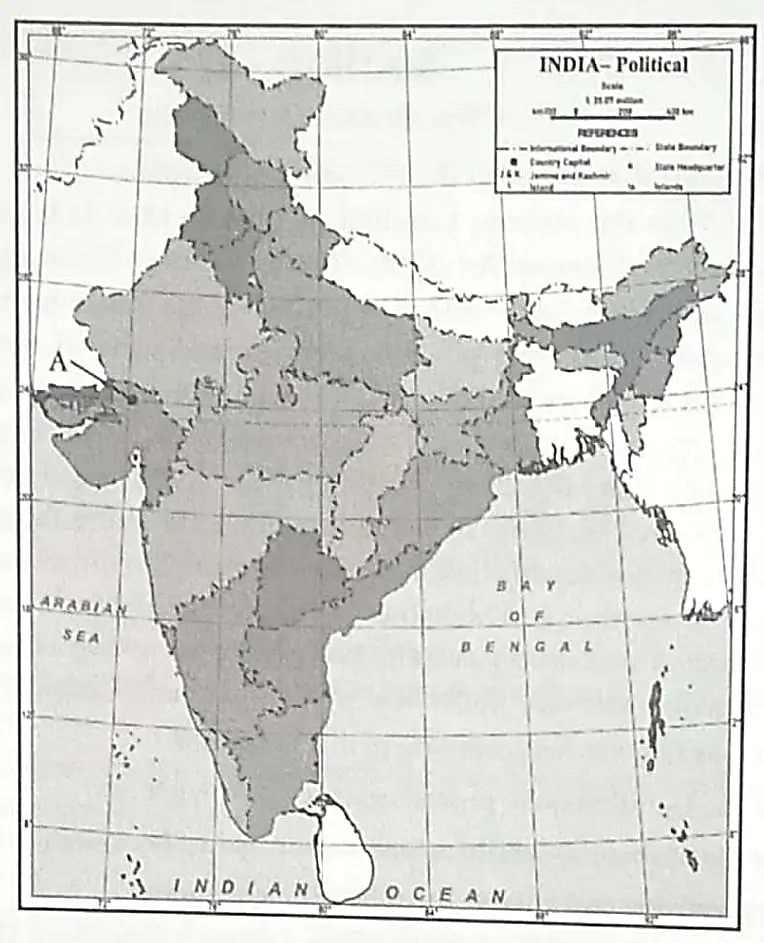
13. 13.1 On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it
(A) The place where cotton mill workers organized Satyagraha in 1918. 1
13.2 On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Namrup Thermal Power Station 1
OR
Salem Iron & Steel Plant 1
(II) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport 1