Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Solved)
Class 10 Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions:
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) The question paper has three sections and 15 questions.
(iii) Section – A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section – B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section – C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
(iv) Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section – A
1. The table shows the electronic structures of four elements. [2]

(a) Identify which element(s) will form covalent bonds with carbon.
(b) “Carbon reacts with an element in the above table to form several compounds.” Give suitable reason.
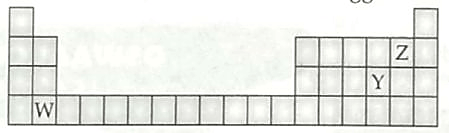
2. The diagram below shows part of the periodic table. [2]
(a) Which elements would react together to form covalent compounds?
(b) Between the two elements W and Z, which will have a bigger atomic radius? Why?
3. (a) Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being released from the penis.
(b) State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote. [2]
4. Rajesh observed a patch of greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread. [2]
(a) Name the organism responsible for this and its specific mode of asexual reproduction.
(b) Name its vegetative and reproductive parts.
5. Mustard was growing in two fields- A and B, while field A produced brown coloured seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds.
It was observed that in field A, the offsprings showed only the parental trait for consecutive generations, whereas in field B, majority of the offsprings showed a variation in the progeny.
What are the probable reasons for these? [2]
OR
In an asexually reproducing species, if a trait X exists in 5% of a population and trait Y exists in 70% of the same population, which of the two traits is likely to have arisen earlier? Give reason.
6. A simple motor is made in a school laboratory. A coil of wire is mounted on an axle between the poles of a horseshoe magnet, as illustrated. [2]
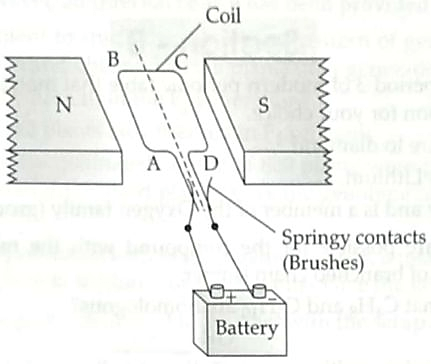
In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as shown.
(a) For this position, state the direction of the force on the arm AB.
(b) Why does the current in the arm BC not contribute to the turning force on the coil?
OR
A circuit contains a battery, a variable resistor and a solenoid. The figure below shows the magnetic field pattern produced by the current in the solenoid.
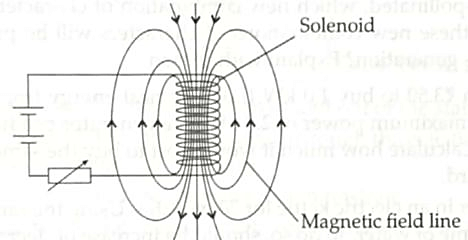
(a) State how the magnetic field pattern indicates regions, where the magnetic field is stronger.
(b) What happens to the magnetic field when the current in the circuit is reversed?
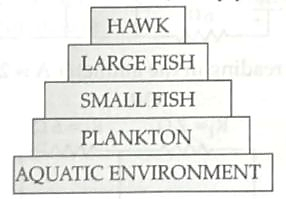
7. DDT was sprayed in a lake to regulate breeding of mosquitoes. How would it affect the trophic levels in the following food chain associated with a lake? Justify your answer. [2]
OR
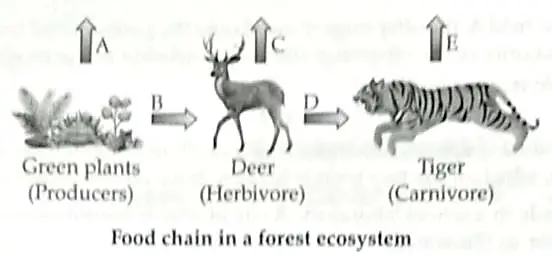
In the following food chain, vertical arrows indicate the energy lost to the environment and horizontal arrows indicate the energy transferred to the next trophic level. Which one of the three vertical arrows (A, C and E) and which one of the two horizontal arrows (B and D) will represent more energy transfer? Give reason for your answer.
Section – B
8. Choose an element from period 3 of modern periodic table that matches the description given below in each instance. Give reason for your choice. [3]
(a) It has a similar structure to diamond.
(b) It has same valency as Lithium.
(c) It has variable valency and is a member of the Oxygen family (group 16).
9. (a) How many isomers are possible for the compound with the molecular formula C4H8? Draw electron dot structure of branched chain isomer.
(b) How will you prove that C4H8 and C5H10 are homologous? [3]
OR
A carbon compound ‘A’ having melting point 156K and boiling point 351K, with molecular formula C2H6O is soluble in water in all proportions.
(a) Identify ‘A’ and draw its electron dot structure.
(b) Give the molecular formulae of any two homologous of ‘A’.
10. Two pea plants-one with round yellow (RRYY) seeds and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total of 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason. [3]
11. (a) It would cost a man ₹3.50 to buy 1.0 kW h of electrical energy from the Main Electricity Board. His generator has a maximum power of 2.0 kW. The generator produces energy at this maximum power for 3 hours. Calculate how much it would cost to buy the same amount of energy from the Main Electricity Board. [1]
(b) A student boils water in an electric kettle for 20 minutes. Using the same mains supply, he wants to reduce the boiling time of water. To do so, should he increase or decrease the length of the heating element? Justify your answer. [2]
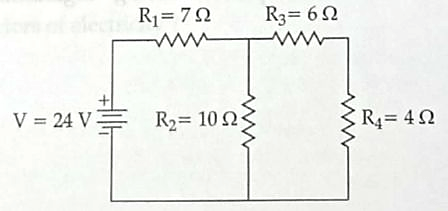
12.
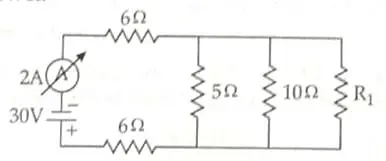
In the above circuit, if the current reading in the ammeter A is 2A, what would be the value of R1? [3]
OR
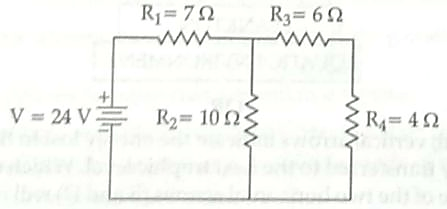
Calculate the total resistance of the circuit and find the total current in the circuit.
13. Gas A, found in the upper layers of the atmosphere, is a deadly poison but is essential for all living beings. The amount of this gas started declining sharply in the 1980’s. [3]
(a) Identify Gas A. How is it formed at higher levels of the atmosphere?
(b) Why is it essential for all living beings? State the cause for the depletion of this gas.
Section – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (a), (b), (c). Parts (a) and (b) are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part (c).
14. Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
(a) What set of genes will be present in the F1 generation? [1]
(b) Give reason, why only tall plants are observed in F1 progeny. [1]
(c) When F1 plants were self – pollinated, a total of 800 plants were produced. How many of these would be tall, medium height or short plants? Give the genotype of F2 generation. [2]
OR
When F1 plants were cross-pollinated with plants having tt genes, a total of 800 plants were produced. How many of these would be tall, medium, or short plants? Give the genotype of F2 generation.
15. Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below. [4]
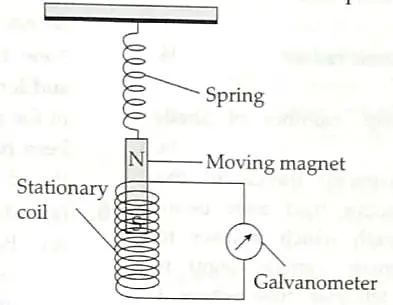
A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil.
He lifted the magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil. Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following questions.
(a) What is the principle which Ansari Sir is trying to demonstrate? [1]
(b) What will be observed when the magnet starts oscillating through the coil. Explain the reason behind this observation. [1]
(c) Consider the situation where the magnet goes in and out of the coil. State two changes which could be made to increase the deflection in the galvanometer. [2]
OR
Is there any difference in the observations in the galvanometer when the magnet swings in and then out of the stationary coil? Justify your answer. [2]
Solution of Sample Paper
Section – A
1. (a) P and R ½ + ½
(b) Carbon has a valency of four or tetravalency & catenation ½ + ½
2. (a) Y and Z 1
(b) W has bigger atomic radius. ½
Reason: Down the group, number of shells increases. ½
3. (a) Male gamete (sperm) travels in the female reproductive tract after being released. The path which it takes to fertilise the female gamete (egg) is vagina, uterus, fallopian tube where it fuses with the egg cell resulting in the formation of a zygote
(Alternative: labelled figure of human female reproductive system indicating the passage of sperm from vagina to uterus and then to fallopian tube for fertilisation, resulting in the formation of a zygote.) 1
(b) Zygote has 2 sets of chromosomes. 1
4. (a) The greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread is due to bread mould (Rhizopus) which reproduces by spore formation. ½ + ½
(b) Hyphae or thread like structures are the vegetative part and tiny blob like structures or sporangia are the reproductive parts. ½ + ½
5. In field A, the reason for parental trait in consecutive generations of the offsprings is self-pollination. 1
In field B, variation is seen because of recombination of genes as cross-pollination is taking place. 1
OR
Trait Y, which exists in 70% (larger fraction) of the population, is likely to have arisen earlier because in asexual reproduction, identical, copies of DNA are produced and variations do not occur. 1
New traits come in the population due to sudden mutation and then are inherited. 70 % of the population with trait Y is likely to have been replicating that trait for a longer period, than 5 % of population with trait X. 1
6. (a) downwards 1
(b) Because BC is in the same direction as the direction of field lines. Force is minimum when the direction of current in the conductor is the same as that of the magnetic field. BC will not contribute as the force on this part of the coil will be cancelled by the force on DA. 1
OR
(a) Relative closeness of field lines indicates the strength of magnetic field. Since, field lines are crowded around the ends of the solenoid, hence these are the regions of strongest magnetism. 1
(b) The direction of the field will also be reversed. 1
7. • DDT being a non-biodegradable pesticide will enter the food chain from the first trophic level i.e, Plankton. ½
• Non-biodegradable pesticides accumulate progressively at each trophic level. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification. 1
• Hawk will have the highest level of pesticide. ½
OR
A will represent more energy transfer as compared to C and E. ½
B will represent more energy transfer as compared to D. ½
When green plants are eaten by primary consumers, a great amount of energy is lost as heat in to the environment, some amount goes into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. An average of 10% of the food eaten is made available for the next level of consumers. This loss of energy takes place at every trophic level. 1
(Alternatively accept- In accordance with 10% law of transfer of energy in a food chain, only 10% of energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level.)
Section – B
8. (a) Silicon
Reason: Tetrahedral structure
OR
Tetravalency or four valency and catenation
OR
Covalent bonding like carbon ½ + ½
(b) Sodium
Reason: It has 1 valence electron like Lithium ½
(c) Sulphur
Reason: It forms oxides SO2 and SO3 ½ + ½
9. (a) Five 1½
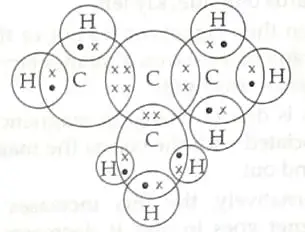
(b) C4H8 and C5H10 are homologous as they differ in ½
• “–CH2–“
• differ in 14u molecular mass
• Same functional group
• Same general formula (Any two reasons) ½ +½
OR
(a) Ethanol; C2H5OH 1 + 1
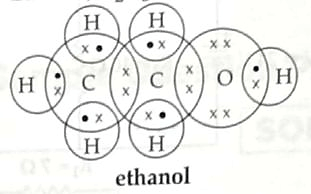
(b) CH3OH and C3H7OH are homologous of ethanol. 1
OR
CH4O and C3H8O 1
10. Round green: 30 ½ + ½
Wrinkled yellow: 30 ½ + ½
New combinations are produced because of the independent inheritance of seed shape and seed colour trait. 1
11. (a) E = P x T
So, E = 3 x 2 = 6 kWh 1
Cost of buying electricity from the main electricity board = 6 x 3.50 = ₹ 21.0
(b) To reduce the boiling time using the same mains supply, the rate of heat production should be large. We know that P = V2/R. Since V is constant, R should be decreased. Since R is directly proportional to L so, length should be decreased. 2
12. 5 ohm, 10 ohm and R1 are in parallel connection
1/Rp = 1/5 + 1/10 + 1/R1
1/Rp = (2 + 1)/10 + 1/R1
= 3/10 + 1/R1
1/Rp = (3R1 + 10)/10R1
Rp = 10R1/(3R1 + 10)
Now, 6 ohm, 6 ohm and Rp are in series
Thus,
Req = 12 + 10 R1(3R1 + 10) …..(i) 1
V = I Req
From the circuit
Req = 30/2 = 15Ω …..(ii) 1
Equating (i) and (ii)
12 + 10 R1/(3R1 + 10) = 15
10R1/(3R1 + 10) = 3
10R1 = (9R1 + 30)
Thus, R1 = 30 ohm 1
OR
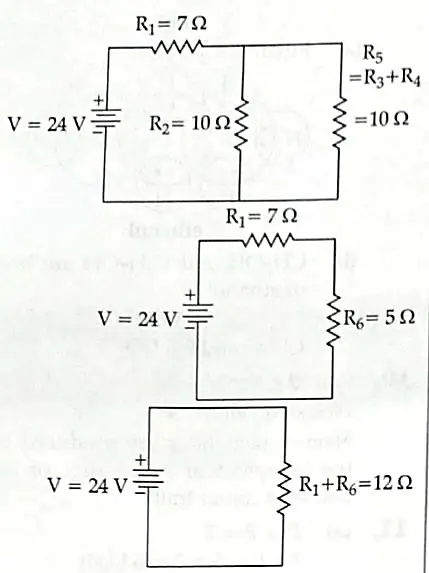
R3 and R4 are in series, hence the equivalent resistance of those two = R5 = R3 + R4 = 10 ohm. ½
R5 and R2 are in parallel, Let R6 be the equivalent resistance for them. Hence, R6 = (R5R2)/(R5 + R2) = 100/20 = 5 ohm ½
Now R1 and R6 are in series and hence the final equivalent resistance of the entire circuit is R = R1 + R6 = 12 ohm. 1
By Ohm’s Law, we know that V = IR, hence I = V/R.
Hence the current in the circuit is 24/12 A = 2A 1
13. (a) Gas A is Ozone. ½
Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on oxygen (O2) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with molecular oxygen to form Ozone. 1
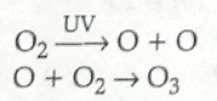
(b) Ozone shields the surface of the earth and protects living organisms from ultraviolet (UV) radiations released by the sun. ½
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) which are used as refrigerants in fire extinguishers lead to depletion of ozone layer. ½ + ½
Section – C
14. (a) Tt 1
(b) Both the recessive and dominant trait are passed on in F1 progeny. Out of the two trait only one of them is able to express itself in the progeny, which is called the dominant (T), while the other one is called the recessive (t). Here, the ‘tall’ trait is the dominant one. 1
(c) Out of 800 plants, 600 plants will be tall and 200 plants will be small.
1 : 2 : 1 (TT : Tt : tt) 1 + 1
OR
In the cross between Tt X tt, 400 Tall (Tt) and 400 short (tt) plants will be produced. 1
1 : 1(Tt : tt) 1
15. (a) Sir is trying to demonstrate the principle of Electromagnetic induction. 1
(b) There will be fluctuating induced current in the coil due to relative motion between the magnet and the coil. Accordingly the galvanometer needle will fluctuate on either side of 0 mark. Changing the magnetic field around the coil generates induced current. 1
(c) Using a stronger magnet, or using a coil with more number of turns. 2
OR
When the magnet moves into the coil, the galvanometer shows a momentary deflection towards one side, say left. ½
When the magnet moves out of the coil, the galvanometer shows a momentary deflection now towards right. ½
This is due to changing magnetic field /flux associated with the coil as the magnet moves in and out.
Alternatively, the flux increases when the magnet goes in and it decreases when the magnet goes out. 1