Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Water Resources
NCERT Notes For Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Water Resources, in this step-by-step answer guide. In some of State Boards and CBSE schools, students are taught thru NCERT books. As the chapter comes to an end, students are requested few questions in an exercising to evaluate their expertise of the chapter.
Students regularly want guidance managing those NCERT Notes. It’s most effective natural to get stuck withinside the exercises while solving them so that you can assist students score higher marks, we’ve provided step by step NCERT answers for all exercises of Class ten Geography so you can be looking for assist from them.
Students should solve those exercises carefully as questions withinside the final exams are requested from those, so these exercises immediately have an impact on students’ final score. Find all NCERT Notes for Class ten Geography below and prepare in your tests easily.
NCERT Notes For Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Water Resources
Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Water Resources
Water
Three-fourth of the earth’s surface is covered with water but only a small proportion of it accounts for freshwater that can be put to use. Water is a renewable resource.
Water Scarcity and the Need for Water Conservation and Management
The availability of water resources varies over space and time.
- Water scarcity is caused by over-exploitation, excessive use and unequal access to water among different social groups.
- Water resources are being over-exploited to expand irrigated areas for dry-season agriculture.
- In some areas, water is sufficiently available to meet the needs of the people. But, those areas still suffer from water scarcity due to bad quality of water.
The need of the hour is to conserve and manage our water resources:
- To safeguard ourselves from health hazards.
- To ensure food security, continuation of our livelihoods and productive activities.
- To prevent degradation of our natural ecosystems.
Multi-Purpose River Projects and Integrated Water Resources Management
- In ancient times, we used to conserve water by constructing sophisticated hydraulic structures like dams built of stone rubble, reservoirs or lakes, embankments and canals for irrigation.
- We have continued this tradition in modern India by building dams in most of our river basins.
Dams
A dam is a barrier across flowing water that obstructs, directs or retards the flow, often creating a reservoir, lake or impoundment. “Dam” refers to the reservoir rather than the structure.
Uses of Dam:
Dams are built:
- To impound rivers and rainwater that can be used later to irrigate agricultural fields.
- For electricity generation.
- Water supply for domestic and industrial uses.
- Flood control.
- Recreation, inland navigation and fish breeding.
Side effects of Creating Dams
- Regulating and damming of rivers affect their natural flow.
- Poorer the habitats for the rivers’ aquatic life.
- Fragment rivers make it difficult for aquatic fauna to migrate.
- Dams created on the floodplains submerge the existing vegetation and soil leading to its decomposition over a period of time.
- Creating of large dams has been the cause of many new environmental movements like the
‘Narmada Bachao Andolan’ and the ‘Tehri Dam Andolan’ etc.
- Many times local people had to give up their land, livelihood and their control over resources for the construction of the dam.
Most of the objections to the projects arose due to their failure to achieve the purposes for which they were built. Most of the dams were constructed to control floods but, these dams have triggered floods. Dams have also caused extensive soil erosion. Excessive use of water has resulted in earthquakes, caused water-borne diseases and pests and pollution.
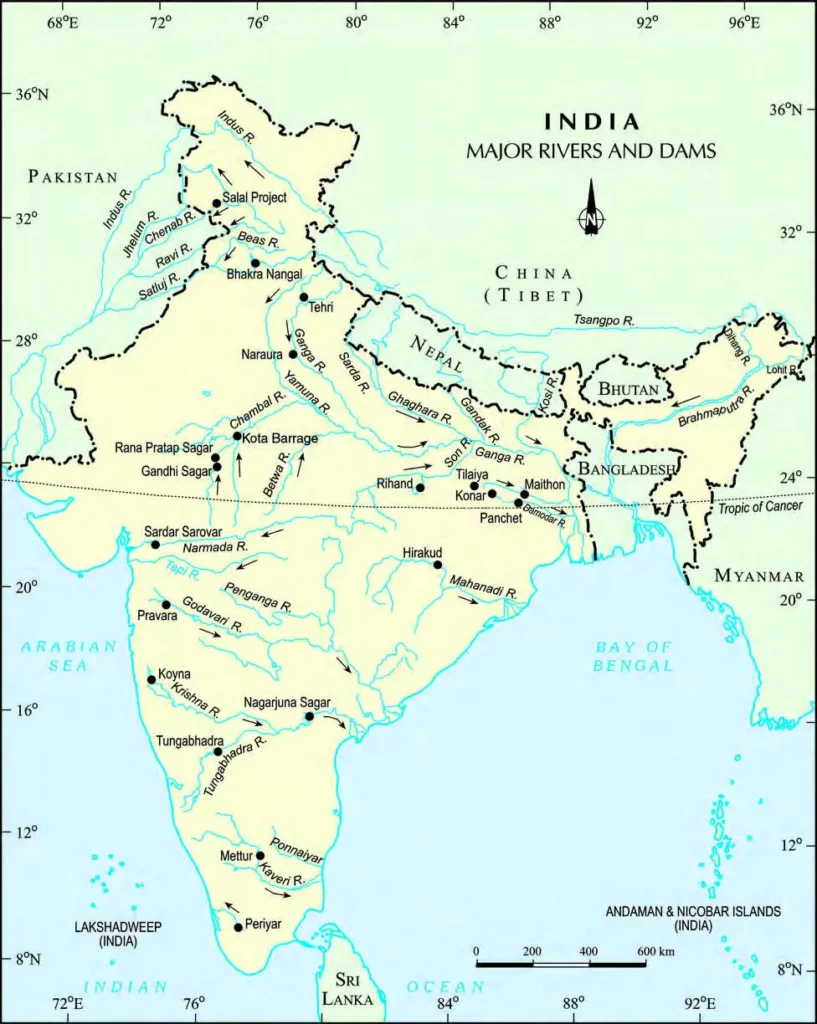
Have a look at the India Major Rivers and Dams in the map below:
Rain Water Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a simple method by which rainfall is collected for future usage. The collected rainwater may be stored, utilised in different ways or directly used for recharge purposes.
Different methods have been adopted in different areas for Rain Water Harvesting.
In hill and mountainous regions, people built diversion channels like the ‘guls’ or ‘kuls’ of the Western Himalayas for agriculture.
- “Rooftop rainwater harvesting” is commonly practised to store drinking water, particularly in Rajasthan.
- In the flood plains of Bengal, people developed inundation channels to irrigate their fields.
- In arid and semi-arid regions, agricultural fields were converted into rain-fed storage structures that allowed the water to stand and moisten the soil such as ‘khadins’ in Jaisalmer and ‘Johads’ in other parts of Rajasthan.
- The tankas are part of the well-developed rooftop rainwater harvesting system and are built inside the main house or the courtyard.
- This is mainly practised in Rajasthan, particularly in Bikaner, Phalodi and Barmer areas for saving the rainwater.
- Many houses constructed underground rooms adjoining the ‘tanka’ to beat the summer heat as it would keep the room cool.
Tamil Nadu is the first state in India which has made rooftop rainwater harvesting structure compulsory to all the houses across the state. There are legal provisions to punish the defaulters.
Class 10 Geography Updated Chapter Notes
Class 10 Update Notes of all subjects
| Class 10 Notes |
| Class 10 Science Notes |
| Class 10 Social Science Notes |
| Class 10 English Summary |
| Class 10 Hindi Summary |
Benefits of NCERT Notes
NCERT’s Class 10 Notes contains extremely important points, and for each chapter, each concept has been simplified to make it easier to remember and increase your chances of achieving excellent exam results. Exam Preparation References Here are some tips on how these Notes can help you prepare for the exam.\
- This helps students solve many of the problems in each chapter and encourages them to make their concepts more meaningful.
- NCERT Notes for Class 10 encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam.
- These Notes are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
- Most of the questions in the exam are formulated in a similar way to NCERT textbooks. Therefore, students should review the solutions in each chapter in order to better understand the topic.
- It is free of cost.
Tips & Strategies for Class 10 Exam Preparation
- Plan your course and syllabus and make time for revision
- Please refer to the NCERT solution available on the cbsestudyguru website to clarify your concepts every time you prepare for the exam.
- Use the cbsestudyguru learning app to start learning to successfully pass the exam. Provide complete teaching materials, including resolved and unresolved tasks.
- It is important to clear all your doubts before the exam with your teachers or Alex (an Al study Bot).
- When you read or study a chapter, write down algorithm formulas, theorems, etc., and review them quickly before the exam.
- Practice an ample number of question papers to make your concepts stronger.
- Take rest and a proper meal. Don’t stress too much.
Why opt for cbsestudyguru NCERT Notes for Class 10 ?
- cbsestudyguru provide NCERT Notes for all subjects at your fingertips.
- These Notes are designed by subject matter experts and provide solutions to every NCERT textbook questions.
- cbsestudyguru especially focuses on making learning interactive, effective and for all classes.
- We provide free NCERT Notes for class 10 and all other classes.