Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Solved)
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Social Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions :
1. This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
2 All questions are compulsory.
3. Section-A: Question no, 1 to 5 are Very Short Answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
4. Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are Short Answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
5. Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are Long Answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
7. Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
(2 x 5 = 10)
1. How did the Non-Cooperation Movement unfold in the cities and towns of India?
2. Why is tourism considered as a trade?
3. Differentiate between one party and two party system.
4. State the role of the Reserve Bank of India.
5. Read the data in the table given below and answer the questions that follows:
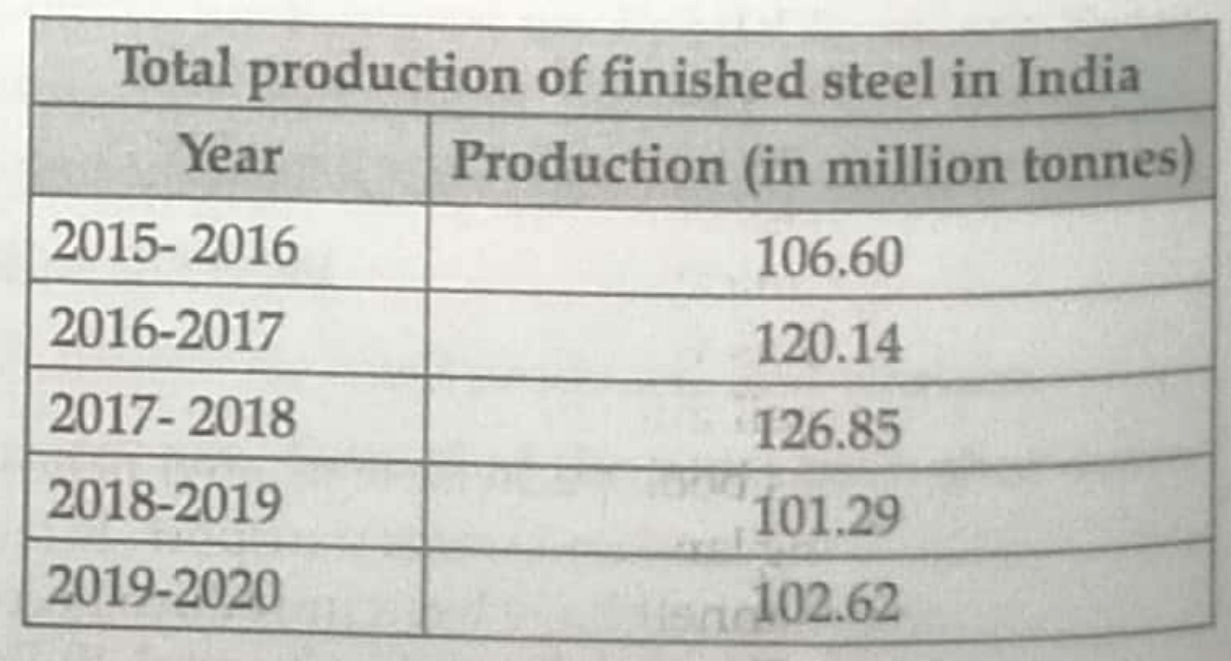
5.1 Compare the 2015-2016 and 2019-2020 data and give any one reason for the reduction of production of steel in 2019- 2020.
5.2 Why is production and consumption of steel considered as an index of a country’s development?
Section B
Short Answer Type Questions
(3 x 3 = 9)
6. Why do most of the rural households still remain dependent on the informal sources of credit? Explain.
OR
How do Self Help Groups help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral? Explain.
7. “Tribal peasants interpreted the message of Mahatma Gandhi and the idea of Swaraj in another way and participated in the Non-Cooperation Movement differently.” Justify the statement.
8. Examine the role of Political Parties in a Democratic country.
Section C
Long Answer Type Questions
(5 x 2 = 10)
9. Democracy’s ability to generate its own support is itself an outcome that cannot be ignored. Support the statement with examples.
OR
‘There is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy in South Asia.’ Support the statement with examples.
10. Examine the role of Information Technology in stimulating the process of globalization.
OR
Assess the impact of globalization on India and its people.
Section – D
Case Based Questions
(4 x 2 = 8)
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions: 4
It is said of “passive resistance” that it is the weapon of the weak, but the power which is the subject of this article can be used only by the strong. This power is not passive resistance; indeed, it calls for intense activity. The movement in South Africa was not passive but active.
‘Satyagraha is not physical force. A Satyagrahi does not inflict pain on the adversary; he does not seek his destruction …. In the use of Satyagraha, there is no ill-will whatever.
“Satyagraha is pure soul-force. Truth is the very substance of the soul. That is why this force is called Satyagraha. The soul is informed with knowledge. In it burns the flame of love. … Non- violence is the supreme dharma …’It is certain that India cannot rival Britain or Europe in force of arms. The British worship the war-god and they can all of them become, as they are becoming, bearers of arms. The hundreds of millions in India can never carry arms. They have made the religion of non-violence their own …’
11.1 Why did Gandhiji consider non-violence as supreme dharma? 1
11.2 How was Gandhian Satyagraha taken by the people who believed in his philosophy? 1
11.3 Why was Gandhian Satyagraha considered as a novel way to resist injustice? 2
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions: 4
Ever since humans appeared on the earth, they have used different means of communication. But, the pace of change, has been rapid in modern times. Long distance communication is far easier without physical movement of the communicator or receiver. Personal communication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films, etc. are the major means of communication in the country. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications. Cards and envelopes are considered first- class mail and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. The second-class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport. To facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel.
12.1 Examine the role of the Indian postal network. 1
12.2 Differentiate between mass communication and personal communication. 1
12.3 Analyse the significance of communication for a nation. 2
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
(1 x 3 = 3)
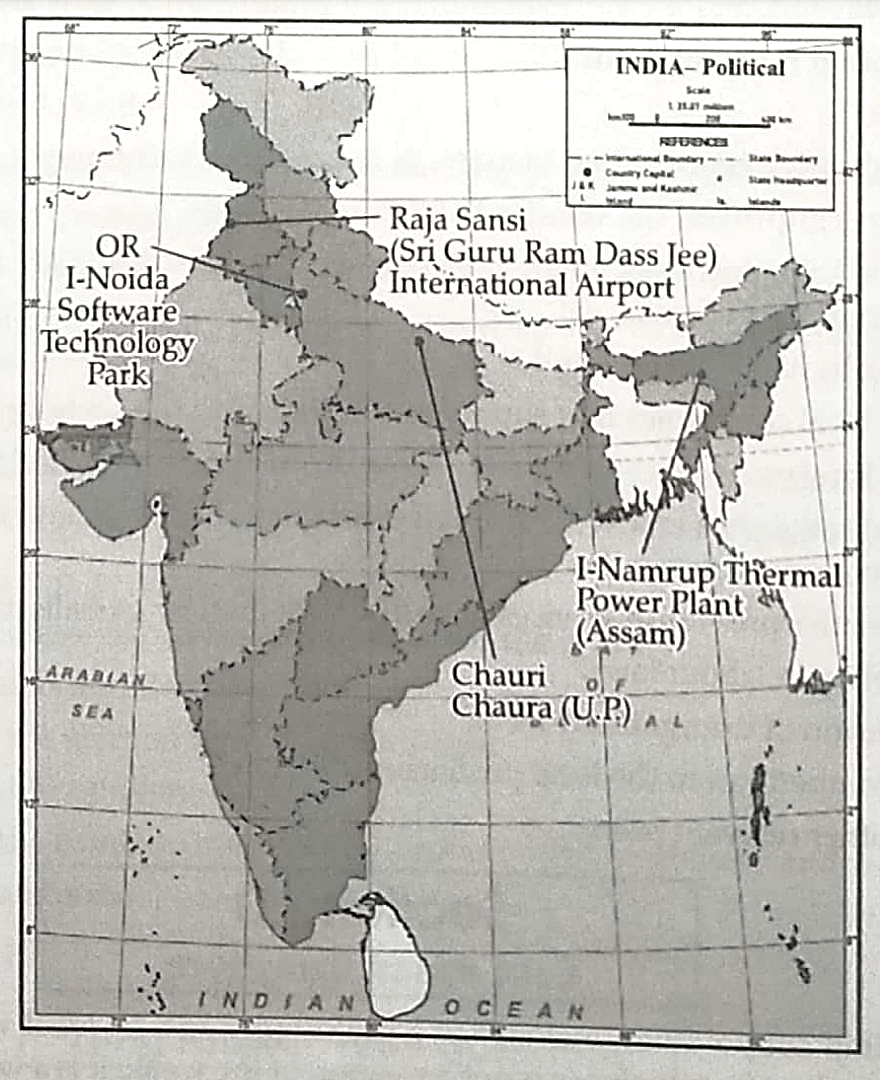
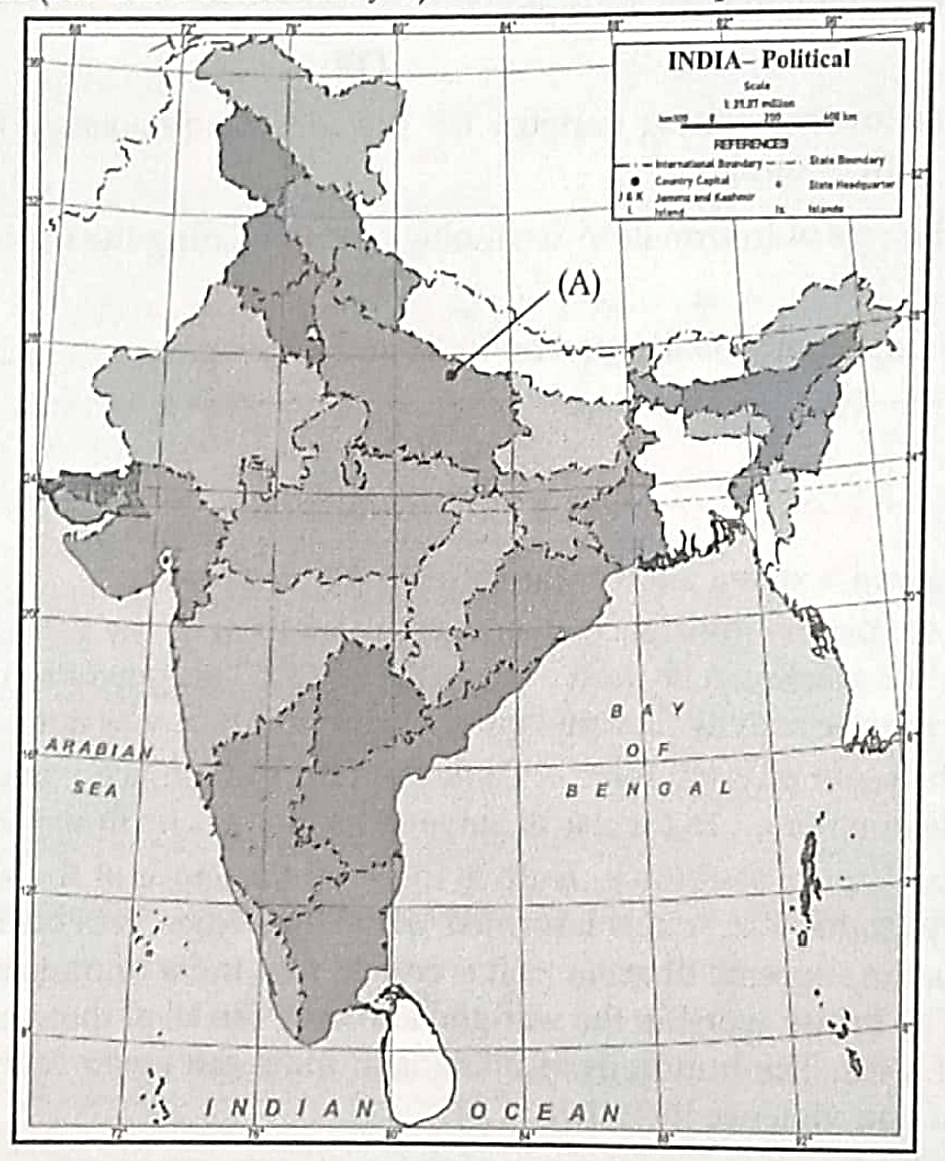
13. 13.1 On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(A) The place where Non-Cooperation Movement was called off due to violence. 1
13.2 On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Namrup Thermal Plant 1
OR
Noida Software Technology Park 1
(II) Raja Sansi (Sri Guru Ram Dass Jee) International Airport 1
Solution of Sample Paper
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
1. (i) The movement started with middle-class participation in the cities.
(ii) Thousands of students left government-controlled schools and college.
(iii) Many teachers resigned.
(iv) Lawyers gave up their legal practices.
(v) The council elections were boycotted in most provinces except Madras.
(vi) Foreign goods were boycotted, liquor shops picketed, and foreign cloth burnt in huge bonfires.
(vii) Any other relevant point. (Any Two Points)
2. (i) Foreign tourist’s arrival in the country contributes to foreign exchange.
(ii) Many people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
(iii) Tourism provides support to local handicrafts.
(iv) Tourists visit India for medical tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism and business tourism.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any Two Points)
3. One Party System
(i) Countries where only one party is allowed to control and run the government are called one party system.
(ii) Eg., In China only Communist Party is allowed to rule.
(iii) Any other relevant point.
Two Party System
(i) Countries where only two main parties contest elections are called Two Party System.
(ii) The United States of America and United Kingdom are examples of Two Party System.
(iii) Any other relevant point. (Any Two Points Each) (½ x 4=2)
4. (i) In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(ii) The RBI supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
(iii) The RBI monitors the banks in actually maintaining cash balance.
(iv) The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any Two Points)
5.1 (i) High costs.
(ii) Limited availability of coking coal.
(iii) Lower productivity of labour.
(iv) Irregular supply of energy.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any One Point)
5.2 (i) The steel products are used as a raw material in different industries.
(ii) It is required for export.
(iii) It provides machinery for ensuring country’s growth.
(iv) Any other relevant point. (Any One Point)
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions
6. (i) Limited availability of banks in rural areas.
(ii) People in the rural areas face problem with regard to documentation.
(iii) Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
(iv) Rural people get easy loans from the richer households through informal ways.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any Three Points)
OR
(i) People can get timely loans for a variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(ii) SHGs are regular in their savings which can be used as monetary help.
(iii) Members can take small loans without collateral to meet their needs.
(iv) Due to timely repayment banks also lend loans to SHGs.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any Three Points)
7. (i) Spread of militant guerrilla movement in the Gudem Hills of Andhra Pradesh.
(ii) They were against colonial policies.
(iii) Their livelihood was affected and their traditional rights were denied.
(iv) Their leader Alluri Sitarama Raju was inspired by the Non-Cooperation Movement and persuaded people to wear khadi and give up drinking.
(v) He wanted liberation by the use of force.
(vi) The rebels attacked police stations and carried on guerrilla warfare for achieving swaraj.
(vii) Any other relevant point (To be evaluated as a whole)
8. (i) Parties form and run governments.
(ii) Parties play a decisive role in making policies for the country.
(iii) They recruit leaders and train them.
(iv) Parties that lose the election form the opposition.
(v) Parties shape public opinion.
(vi) Parties provide the common man access to government machinery and welfare schemes.
(vii) Any other relevant point. (Any Three Points)
Section C
Long Answer Type Questions
9. (i) Democracy ensures that decision making is based on norms and procedure.
(ii) Every citizen has the right and means to examine the process of decision making.
(iii) Democratic Governments are accountable, legitimate and transparent governments.
(iv) People have the right to choose their rulers.
(v) Democracy gives its citizens the right to information about the government and its functioning
(vi) A Democratic Government is the people’s own government and it is run by the people.
(vii) Any other relevant point. (Any Five Points)
OR
(i) Democratic Government is people’s own government.
(ii) Countries from South Asia want democratic rights for people.
(iii) Countries want to elect their representatives by themselves.
(iv) Democracy provides dignity and freedom to its citizens.
(v) Democracy accommodates social diversity.
(vi) Democracy is based on the idea of discussion and negotiation.
(vi) E.g., India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan
(vii) Any other relevant point. (Any Five Points)
10. (i) Technology has been changing rapidly.
(ii) Telecommunication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact and access information.
(iii) Helps to communicate from remote areas.
(iv) Development of satellite communication devices.
(v) Computers have now entered almost every field of activity.
(vi) One can obtain and share information through internet.
(vii) Electronic mail (e-mail) and talk (voice-mail) across the world at negligible costs
(viii) Has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries
(ix) Any other relevant point. (Any Five Points)
OR
(i) Globalization has resulted in more choices for the consumers.
(ii) This has improved the standard of living of people.
(iii) MNCs have increased their investments in industries such as cell-phones, automobiles, electronics, soft drinks, etc.
(iv) New jobs have been created.
(v) Some local companies that supply raw materials to MNCs have also benefited.
(vi) Some local companies have been able to invest in newer technology and production methods.
(vii) Globalisation has enabled some large companies such as Tata Motors, Infosys to emerge as multinational companies.
(viii) Companies providing services have also benefited by globalisation.
(ix) Flexibility in labour laws.
(x) Expansion of unorganised sector.
(xi) Stiff competition to the local producers.
(xii) Any other relevant point. (Any Five Points)
Section – D
Case Based Questions
11. 11.1 Gandhiji adopted non-violence as a philosophy and an ideal way of life. According to him philosophy of nonviolence is not a weapon of the weak; it is a weapon, which can be tried by all.
11.2 A Satyagrahi does not inflict pain on the adversary; he does not seek his destruction. In the use of Satyagraha, there is no ill-will.
11.3 (i) One could win the battle through nonviolence.
(ii) This could be done by appealing to the conscience of the oppressor.
(iii) People – including the oppressors – had to be persuaded to see the truth, instead of being forced to accept truth through the use of violence.
(iv) Any other relevant point. (Any Two Points)
12. 12.1 (i) It has helped the country to engage in communication and social-economic development.
(ii) It provides various facilities like speed post, business post, registered post, ordinary post.
(iii) Any other relevant point. (Any One)
12.2 (i) Mass Communication is the medium which provides entertainment as well as creates awareness among the masses. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books, films, etc., whereas Personal Communication is between person to person.
(ii) Any other relevant point. (Any One)
12.3 (i) This is the age of communication using the telephone, television, films, and the Internet.
(ii) Even books, magazines and newspapers are important means of communication.
(iii) Various means of communication have connected the world closer.
(iv) It is the source of entertainment and knowledge.
(v) Any other relevant point. (Any One)
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
13.1 (A) Chauri Chaura (UP)
13.2