Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Solved)
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Social Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions :
1. This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
2 All questions are compulsory.
3. Section-A: Question no, 1 to 5 are Very Short Answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
4. Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are Short Answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
5. Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are Long Answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
7. Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
(2 x 5 = 10)
1. Describe any two main features of the ‘Salt March’.
2. What are Software Technology Parks? State any two points of significance of Information Technology industry in India?
3. Suggest any two effective measures to reform Political Parties.
4. Why do banks or lenders demand collateral against loans?
5. Read the data in the chart given below and answer the questions that follow:
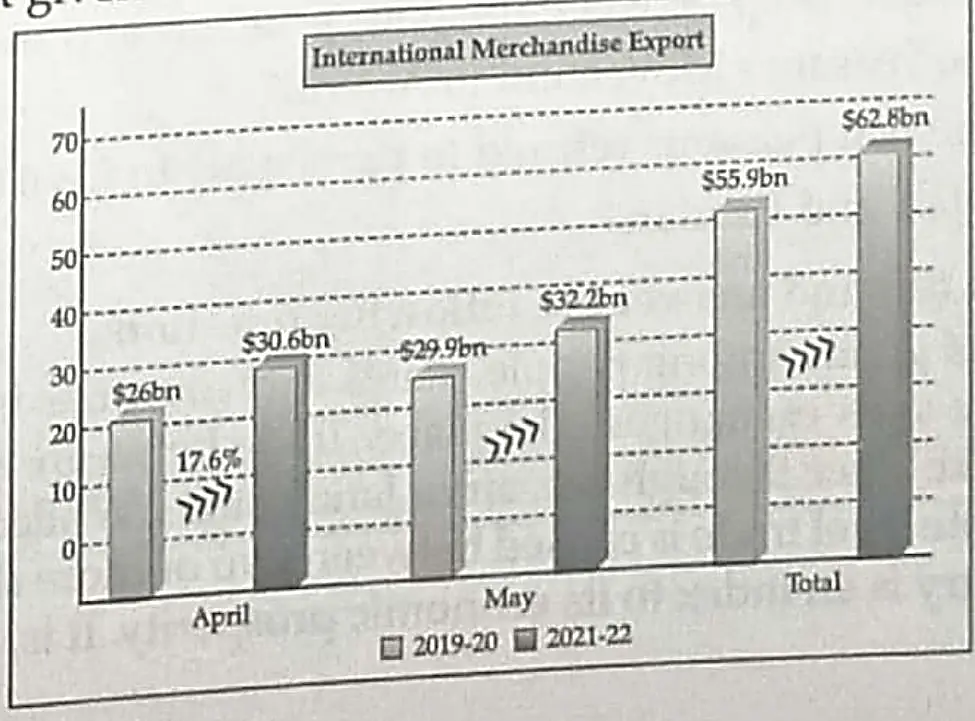
5.1 The above graph is indicating India’s cotton, jute exports which show positive growth. Although it faces a few challenges. Explain any two main challenges faced by the Jute Industry in India.
5.2 Explain any two objectives of National Jute Policy.
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions
(3 x 3 = 9)
6. Why did Europeans flee to America in the nineteenth century. Explain.
7. Why has political funding become a threat for Democracy?
8. How can the benefits of Globalisation be shared better? Explain.
OR
Explain any three loan activities of banks in India.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions
(5 x 2 = 10)
9. “Democracy plays an important role to accommodate social diversity.” Support the statement with examples.
10. Why is it necessary for banks and cooperatives to increase their lending in rural areas? Explain.
OR
Describe the positive impacts of globalisation on Indian economy with examples.
Section – D
Case Based Questions
(4 x 2 = 8)
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions: 4
In the countryside, rich peasant communities – like the Patidars of Gujarat and the Jats of Uttar Pradesh – were active in the movement. Being producers of commercial crops, they were very hard hit by the trade depression and falling prices. As their cash income disappeared, they found it impossible to pay the government’s revenue demand. And the refusal of the government to reduce the revenue demand led to widespread resentment. These rich peasants became enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement, organising their communities and at times forcing reluctant members, to participate in the boycott programmes. For them the fight for Swaraj was a struggle against high revenues. But they were deeply disappointed when the movement was called off in 1931 without the revenue rates being revised. So, when the movement was restarted in 1932, many of them refused to participate.
The poorer peasantry were not just interested in the lowering of the revenue demand. Many of them were small tenants cultivating land they had rented from landlords. As the Depression continued and cash incomes dwindled, the small tenants found it difficult to pay their rent. They wanted the unpaid rent to the landlord to be remitted. They joined a variety of radical movements, often led by Socialists and Communists. Apprehensive of raising issues that might upset the rich peasants and landlords, the Congress was unwilling to support ‘no rent’ campaigns in most places. So, the relationship between the poor peasants and the Congress remained uncertain.
11.1 Who led the Peasant’s Movement in Awadh? 1
11.2 Why did the rich peasants refused to participate in Civil Disobedience Movement in 1932? 1
11.3. Who were Jats and Patidars? 2
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions: 4
The exchange of goods among people, states and countries is referred to as trade. The market is the place where such exchanges take place. Trade between two countries is called international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. While local trade is carried in cities, towns and villages, state level trade is carried between two or more states, Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic barometer for a country. As the resources are space bound, no country can survive without international trade. Export and import are the components of trade. The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and import. When the value of exports exceeds the value of imports, it is called a favourable balance of trade. On the contrary, if the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
India has trade relations with all the major trading blocks and all geographical regions of the world. Among the world, the commodities exported from India to other countries include gems and jewellery, chemicals and related products, agriculture and allied products, etc.
The commodities imported to India include petroleum crude and products, gems and jewellery, chemicals and related products, base metals, electronic items, machinery, agriculture and allied products. India has emerged as a software giant at the international level and it is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology.
12.1 What are the components of the trade? Which is consider the economic barometer of a country? 1
12.2 What are the things imported to India? 1
12.3 What is international trade? 2
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
(1 x 3 = 3)
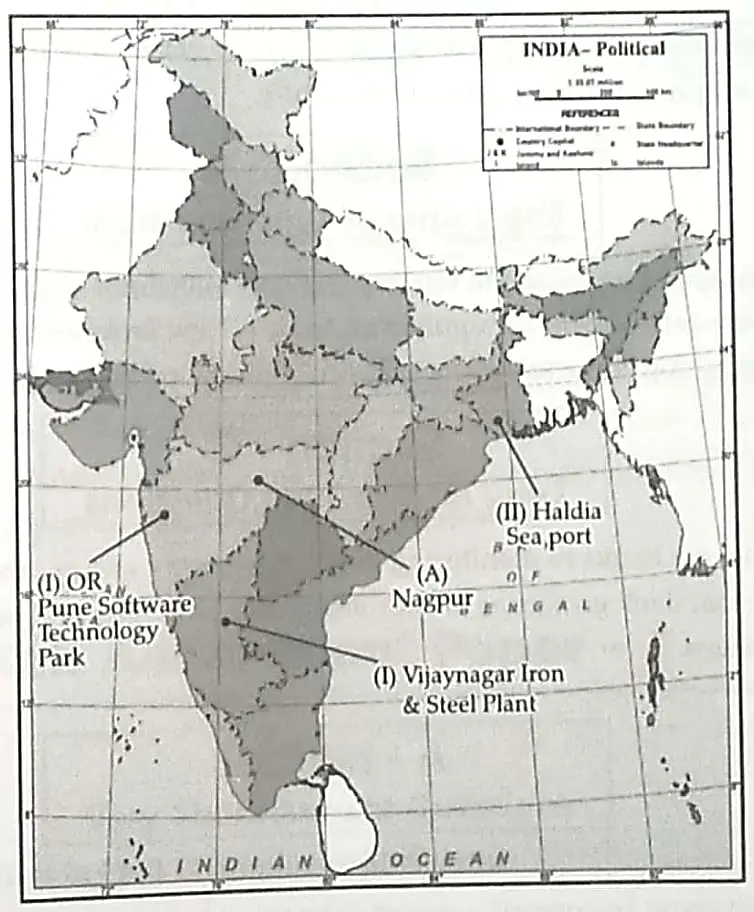
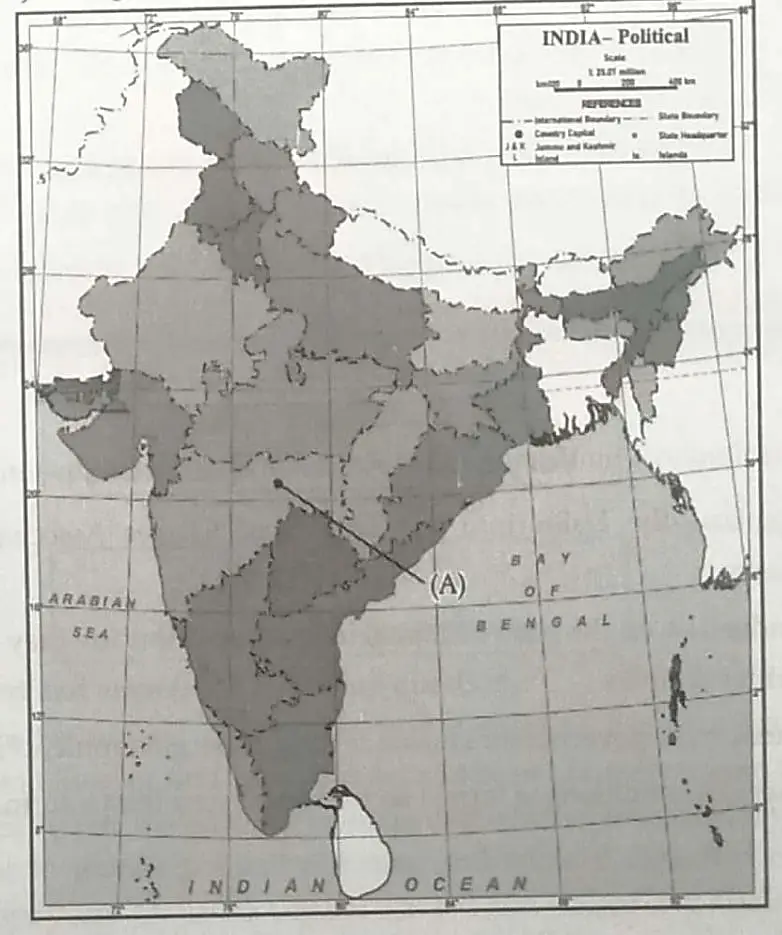
13. 13.1 On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(A) The place where Indian National Congress Session was held in 1920. 1
13.2 On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Vijayanagar Steel Plant 1
OR
Pune Software Technology Park 1
(II) Haldia Major Seaport 1
Solution of Sample Paper
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
1. (i) On 11h March, 1930, Mahatma Gandhi started his famous Salt March’ accompanied by 78 of his trusted volunteers.
(ii) He ceremonially violated the salt law by manufacturing salt by boiling sea water. This marked the beginning of Civil Disobedience Movement. (1 x 2 = 2)
2. Software Technology Park: Software Technology parks provide single window service and high data communication facility to software experts.
Significance of IT industry:
(i) A major impact of this industry has been an employment generation. Up to 31st March, 2005, the IT industry employed over one million persons.
(ii) It is encouraging to know that 30 per cent of the people employed in this sector are Women.
3. Effective measures to reform Political Parties are:
(i) A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of Political Parties.
(ii) It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its members
(iii) It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about 1/3rd to its women candidates.
(iv) There should be a quota for women in the decision making bodies of the Party (Any Two Points) (1 x 2 = 2)
4. Collateral is demanded by the banks or lenders before granting a loan as it is an asset that is owned by the borrower and it can be used as a guarantee to the banks until the loan is repaid. The banks can sell the collateral in case the borrower is unable to pay off his loan. (2)
5.1 Challenges faced by the jute industry are:
(i) Stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes.
(ii) To stimulate demand the products need to be diversified.
(iii) The cost of production is very high. (Any Two Points) (1 x 2 = 2)
5.2 Objective of National Jute Policy:
(i) Increasing productivity.
(ii) Improving quality.
(iii) Ensuring good prices to the jute farmers.
(iv) Enhancing the yield per hectare. (1)
Section B
Short Answer Type Questions
6. Europeans fled to America in the 19th Century because:
(i) Until the 19th Century, poverty and hunger were common in Europe.
(ii) Cities were crowded and deadly diseases were widespread.
(iii) Religious conflicts were common and religious dissenters were persecuted.
(iv) Scrapping of Corn Laws, led to inability of British agriculture to compete with imports.
(v) Thousands of people were left unemployed due to agricultural land lying uncultivated. So, people migrated in thousands, crossed oceans to find employment and a better future.
(vi) In America, plantations were growing cotton and sugar for the European market. These plantations were worked on by slaves. (3)
7. Political Funding has became a threat for Democracy due to the following reasons:
(i) Since parties are focused only on winning elections they tend to use short-cuts and nominate these candidates who have or can raise lots of money. This in twin means lack of experienced and comparatively more suitable candidates in the party.
(ii) Rich people and companies who give funds to the parties tend to have influence on the policies and decisions made by the party.
(iii) As most political parties are dependent on money from rich people and companies, the poor and middle classes do not agree to participate in the electoral process. Hence a majority of people keep away from politics and have little voice in it. (1 x 3 = 3)
8. The benefits of Globalisation can be shared better in the following ways:
(i) The government policy must protect the interest, not only of the rich and the powerful, but of all the people in the country.
(ii) The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights.
(iii) It can support small producers to improve their performance till they become strong enough to compete.
(iv) It can use trade and investment barriers.
(v) It can negotiate at the WTO for ‘fairer rules’. (3)
OR
Loan activities of Banks in India:
(i) Banks use the major portion of the deposits to extend loans.
(ii) Banks make use of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
(iii) Banks mediate between those who have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers).
(iv) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what it offers on deposits. (Any three) (3)
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions
9. Democracy accommodates social Diversities:
(i) Democracy develops a procedure to conduct competition between various social groups. Democracy ensures that every citizen has a chance of being in majority at some point in time.
(ii) In a democracy, different communities can peacefully voice their grievances.
(ii) In democracy the majority needs to work with minority and therefore special rights are provided to minorities.
(iv) Example:
(a) Belgium has successfully negotiated differences among its ethnic population. This reduces the possibility of tensions.
(b) In countries like India, accommodation of social division has been done by providing political power to certain backward classes. (5)
10. It is necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas:
(i) Dependence on informal sources of credit reduces.
(ii) To provide more loan facilities to rural households.
(iii) To save rural people from exploitation.
(iv) It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
(v) The bank and the cooperative societies have to increase the lending facilities to improve the livelihood of the people in the rural areas. (1 x 5 = 5)
OR
Positive impacts of Globalization on Indian economy:
(i) Higher standard of living in urban areas.
(ii) There is a greater choice before the consumers who now enjoy the improved quality and lower prices for several products.
(iii) MNCs have increased their investments in India leading to more job opportunities.
(iv) Globalisation has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as MNCs themselves like Tata Motors, Infosys, Ranbaxy, Asian Paints, etc.
(v) Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services particularly those involving IT (Information Technology). For example, the Indian company producing a magazine for the London based company and call centres.
(vi) Local companies supply raw materials to foreign industries and have prospered. (5)
Section – D
Case Based Questions
11. 11.1 Baba Ramchandra. (1)
11.2 These rich peasants became enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement, organising their communities and at times forcing reluctant members, to participate in the boycott programmes. For them the fight for Swaraj was a struggle against high revenues. But they were deeply disappointed when the movement was called off in 1931 without the revenue rates being revised. So, when the movement was restarted in 1932, many of them refused to participate. (2)
11.3. The Patidars of Gujarat and the Jats of Uttar Pradesh – were rich peasant communities. (1)
12. 12.1 Export and import are the components of trade. The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and import. When the value of exports exceeds the value of imports, it is called a favourable balance of trade. On the contrary, if the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic barometer for a country. (2)
12.2. The commodities imported to India include petroleum crude and products, gems and jewellery, chemicals and related products, base metals, electronic items, machinery, agriculture and allied products. (1)
12.3. Trade between two countries is called international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. (1)
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
13.1 (A) Nagpur.
13.2