Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Solved)
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Social Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions :
1. This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
2 All questions are compulsory.
3. Section-A: Question no, 1 to 5 are Very Short Answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
4. Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are Short Answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
5. Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are Long Answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
7. Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
8. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
9. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
(2 x 5 = 10)
1. Describe the role of ‘Jobbers’ in the beginning of 20h century in India.
2. Classify industries on the basis of ownership and give one example of each category.
3. What are the expected outcomes of Democracy? Explain.
4. Which type of deposits with the banks are called Demand Deposits? State any one important feature of Demand Deposits.
5. Read the data in the chart or diagram given below and answer the questions that follows:
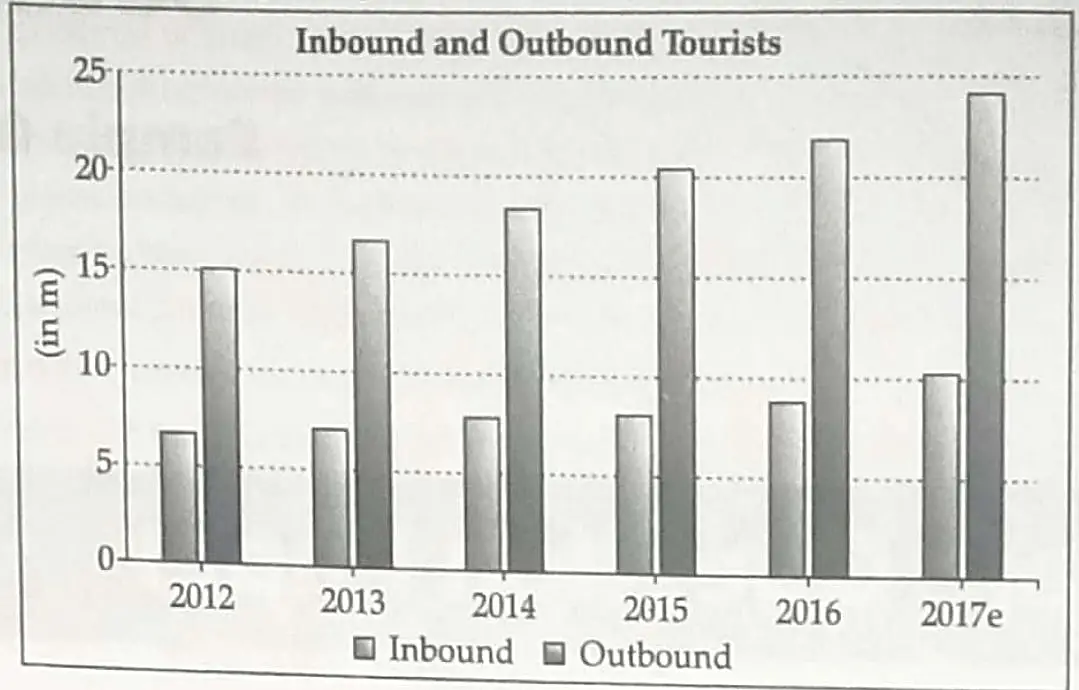
5.1 Give one reason why the tourism industry has grown over a decade in India?
5.2 What industries and services has been supported by tourism?
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions
(3 x 3 = 9)
6. In the 17th century, merchants from towns in Europe began employing peasants and artisans within the villages. Explain.
7. “Democratic governments in practice are known as accountable.” Support the statement with arguments.
8. Why do banks and co-operative societies need to lend more? Explain.
OR
“The impact of Globalization has not been uniform.” Explain with examples.
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions
(5 x 2 = 10)
9. “Political parties are rightly called the government in disguise.” Justify the statement in reference to democratic politics by giving five arguments.
10. How are deposits with the bank beneficial for individual as well as for the nation? Explain with examples.
OR
Explain any five facilities available in the special economic zones developed by the Central and State Governments to attract foreign investment.
Section – D
Case Based Questions
(4 x 2 = 8)
11. Read the given text and answer the following questions: 4
A range of products could be produced only with hand labour. Machines were oriented to produce uniforms, standardised goods with intricate designs and specific shapes. In mid-nineteenth century Britain, for instance, 500 varieties of hammers were produced along with 45 kinds of axes. These required human skill and not Mechanical Technology.
In Victorian Britain, the upper classes – the Aristocrats and the Bourgeoisie – preferred things produced by hand. Handmade products came to symbolise refinement and class. They were better finished, individually produced and carefully designed. Machine made goods were for export to the Colonies.
In countries with labour shortage, industrialists were keen on using mechanical power so that the need for human labour can be minimized. This was the case in nineteenth-century America. Britain, however, had no problem hiring human hands.
11.1 Which were standardised products produced for a mass market? 1
11.2 Who were considered as the upper classes in Victorian Britain ? 1
11.3 Why were homemade products popular among upper classes? 2
12. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced? Some suggestions are: Minimizing the use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages. Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements. Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
Primary treatment by mechanical means: It involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation. Secondary treatment by biological process. Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water. Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industry where there is a threat to groundwater resources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones.
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
12.1 Treatment from industrial effluents can be done in how many stages? 1
12.2 What could be done to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment? 1
12.3. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced? 2
Section E
Map Skill Based Question
(1 x 3 = 3)
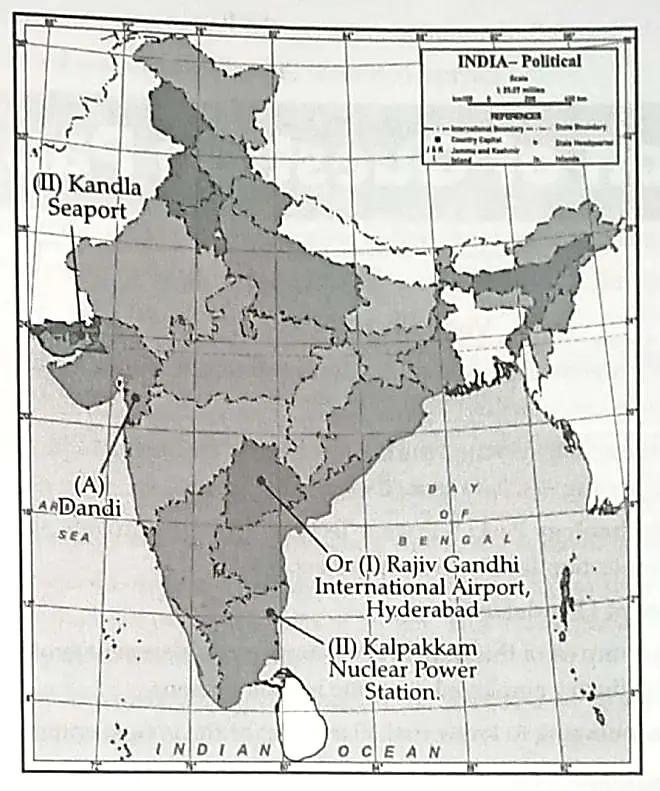
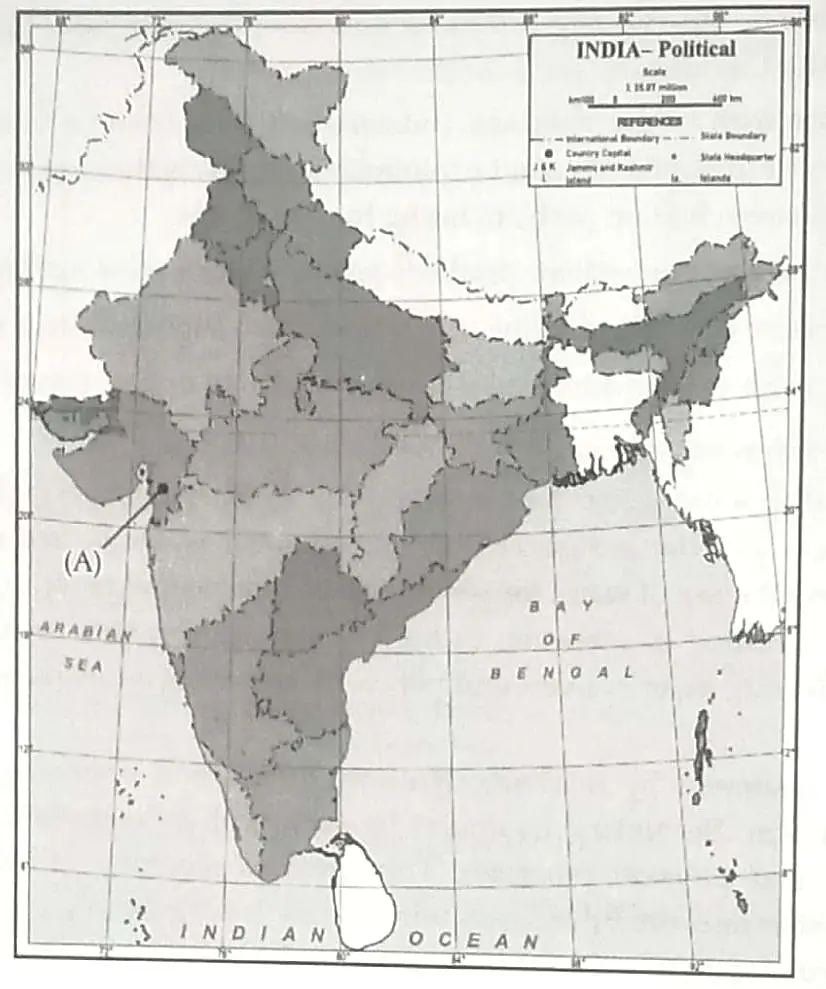
13. 13.1 On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(A) The place where Civil Disobedience Movement was started. 1
13.2 On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(I) Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Station. 1
OR
Rajiv Gandhi International Airport.
(II) Kandla major seaport 1
Solution of Sample Paper
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
1. Role of Jobbers:
Industrialists usually employed jobbers to get new recruits. They became persons with same authority and power. They were old and trusted workers. They got people from their villages. They ensured them jobs. They helped them to settle in the city. They also provided them money in times of crisis. (2)
2. Classification of industries on the basis of ownership:
(i) Public Sector Industries: BHEL, SAIL, etc.
(ii) Private Sector Industries: TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd.
(iii) Joint Sector Industries: Oil India Ltd.
(iv) Cooperative Sector Industries: Sugar Industry in Maharashtra; AMUL, etc. (Any Two Points) (1 x 2 = 2)
3. The expected outcomes of democracy are as follows:
(i) A government that is chosen and accountable to the people is called a Democratic Government.
(ii) A government that is responsive to the needs of the people.
(iii) Economic growth and development reducing all forms of Inequality and end of Poverty. (2)
4. A demand deposit account is a bank account where you can withdraw any time you want, without paying any additional charges for it.
Its important features are:
(i) Banks accept the deposits and also pay an interest rate on the deposits. In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it also earns interest.
(ii) The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash. Since, demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy. (Any One Point) (1+1=2)
5.1 Tourism Industry in India has grown substantially over the last three decades:
(i) Foreign tourism arrival in the country had seen an increased inflow of foreign exchange.
(ii) More than 15 million people are directly engaged in tourism industry.
(iii) Tourism also promotes national integration and provides support to Local Handicrafts. (Any One Point) (1)
5.2 Tourism promotes various industries like handicraft industry, sculpture, seashell, regional handloom among others. Indian handicraft and handloom in particular hold a special attraction for the western tourists. (1)
Section – B
Short Answer Type Questions
6. Merchants from towns in Europe began employing peasants and artisans within the villages as:
(i) Cottagers and villagers were looking for new alternatives of income.
(ii) Tiny plots of land with the villagers could not provide work for all members of the family.
(iii) Advances offered by the merchants made the villagers readily agree to produce goods for them.
(iv) By working for the merchants, they could continue to remain in the villages and do cultivation also.
(v) It was possible to have full use of family labour force. (Any Three Points) (1 x 3 = 3)
7. Democratic governments in practice are accountable because:
(i) It is right to expect Democracy to form a government that follows procedures and is accountable to the people.
(ii) It is also expected that the Democratic Government develops mechanisms for citizens to take part in decision making whenever they think it is fit.
(iii) The Democratic Government is accountable to the people. If it ignores the will of the people, they will not elect their ruler in the next General Election.
(iv) The procedures and decision-making process should be transparent for a democratic government to be accountable to the people. (3)
8. Banks and cooperative societies need to lend more as:
(i) This would lead to higher incomes.
(ii) People would be able to borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(iii) They would be able to grow crops and set up small-scale industries, etc.
(iv) Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.
(v) To save and reduce the dependence on informal sources of credit.
(vi) It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans. (3)
OR
While Globalisation has benefited well off consumers and also producers with skill, education and wealth, many small producers and workers have suffered as a result of the rising competition. Removal of trade barriers and liberalisation policies of the governments to facilitate globalisation have hit the local producers and manufactures hard. Globalisation and the pressure of competition have changed the lives of workers. Faced with growing competition, most employers these days prefer to employ workers ‘flexibly’. This means that workers’ jobs are no longer secure. E.g. MNCs and workers, MNC’s and local manufactures/industries, withdrawal of subsidies, etc. (3)
Section – C
Long Answer Type Questions
9. Political parties perform many crucial functions in democracy.
(i) It contest elections parties choose candidates to contest elections. The process of choosing candidates varies, e.g, in the USA, party members choose the candidates while in India top party leaders choose.
(ii) It puts forward policies and programmes and people choose them. They pile up similar opinions into a major stances that the parties support usually on the line of the ruling.
(iii) They make laws. Legislature makes laws since the majority of the members are from a party, they go by the lines parties take. Moreover, they train and make people (party members) leaders who constitutes the executive.
(iv) Parties form and run governments. Parties recruit leaders, train them and then ministers to run government in the way they want.
(v) They form oppositions. They play their role by voicing different views and criticising government for its failures or wrong policies. They also mobilise opposition to the government. (1 x 5 = 5)
10. The deposits with banks are beneficial for the individual as well as for the nation:
(i) Banks accept deposit and also pay an amount as interest and in this way people earn money.
(ii) People’s money is safe with banks.
(iii) It is easy for individuals to get credit who have savings and current account in the banks.
(iv) Poor people who are engaged in production need credit.
(v) Credit provided by the banks for government projects helps in the development of the nation.
(vi) Banks provide loans for the promotion of International trade.
(vii) Development of infrastructure is undertaken with the loans provided by the banks. (5)
OR
Five facilities available in the Special Economic ones (SEZs) by the central and state governments to attract foreign investment are:
(i) Duty free import and domestic procurement of goods for the development, operation and maintenance of the company.
(ii) 100 percent income tax exemption on export income for first five years, 50 percent for five years thereafter, and 50 percent of the export profit reinvested in the business for the next five years.
(iii) Exemption from the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and levies imposed by state government. Supplies to SEZs are zero rated under the IGST Act, 2017, meaning they are not taxed.
(iv) External commercial borrowing (ECB) is allowed up to US$500 million a year without restriction. For developers of an SEZ, the ECB channel may be availed after receiving government approval, and only for providing infrastructure facilities in the zone. However, ECB will not be permissible for development of integrated township and commercial real estate within the SEZ.
(v) Permission to manufacture products directly, as long as the goods you are producing fall within a sector which allows 100 percent FDI. (5)
Section – D
Case Based Questions
11. 11.1 Uniforms. (1)
11.2 Aristocrats and bourgeoisie were considered as the upper classes. (1)
11.3 In Victorian Britain, the upper classes preferred things produced by hand because handmade products came to symbolise refinement and class. They were better finished, individually produced and carefully designed. (2)
12. 12.1 Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary. (1)
12.2 In order to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment generators fitted with silencers can be used. (1)
12.3 (i) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(ii) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds. Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases.
(iii) Primary treatment by mechanical means: It involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(iv) Secondary treatment by biological process. Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of waste water. (2) (Any one)
Section – E
Map Skill Based Question
13.1 (A) Dandi
13.2