Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022 (Unsolved)
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022, (Social Science) exams are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of the state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students to prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions, and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided a step-by-step NCERT Sample Question Papers for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answer the questions right.
Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Sample Paper 2022
General Instructions:
(i) This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E
(ii) All questions are compulsory.
(iii) Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
(iv) Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
(v) Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
(vi) Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
(vii) Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
(viii) There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
(ix) In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
SECTION – A
(Very Short Answer Type Questions)
[2 x 5 = 10]
1. Mahatma Gandhi said that this feature of the British government revealed its most oppressive face. Identify this feature. 2
2. Define the agglomeration economy. 2
3. Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings, and do not conduct internal elections regularly. Identify this challenge to political parties. 2
4. Read the following data.

In terms of survey on the effects of Globalisation in various sectors on 25 countries, these were the results. Answer the following questions.
(A) Which sector has been affected by Globalisation in the negative way the most? 1
(B) Which sector has been affected by Globalisation equally in positive and negative manner? 1
5. How do Non-democratic regimes react to social differences? 2
SECTION – B
(Short Answer Type Questions)
[3 x 3 = 9]
6. The first image of Bharat Mata created in the twentieth century. Enlist some of its features. 3
7. Is the WTO responsible for smoothening the process of foreign trade across various countries? Has it been successful in doing so?
OR
The RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, to small borrowers etc. What are the other functions of the RBI? 3
8. How can we increase transparency in a democracy? 3
SECTION – C
(Long Answer Type Questions)
[5 x 2 = 10]
9. What is the function of Election Commission mention a few reforms suggested by the Election Commission to change the nature of Indian politics.
OR
Analyse the reception of the Non- Cooperation movement by middle classes in cities and towns. 5
10. India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in length. Mention in detail at least five national waterways.
OR
Critically analyse the impact of rising competition on native markets and producers. 5
SECTION – D
(Case Based Questions)
[4 x 2 = 8]
11. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Why is it so? Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources. As we saw for Megha, bank loans require proper documents and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans. Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence are often willing to give a loan without collateral. The borrowers can, if necessary, approach the moneylender even without repaying their earlier loans. However, the moneylenders charge very high rates of interest, keep no records of the transactions and harass the poor borrowers. In recert years, people have tried out some newer ways of providing loans to the poor.
(A) Why are moneylenders willing to lend without collateral? 1
(B) How is a bank able to lend money to people? 2
(C) What types of borrowers are ideal borrowers for banks? 1
12. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Industrial locations are complex in nature. These are influenced by availability of raw material labour, capital, power, and market. etc. It is rarely possible to find all these factors available at one place Consequently, manufacturing activity tends to locate at the most appropriate place where all the factors of industrial location are either available or can be arranged at lower cost. After industrial activity starts, urbanisation follows. Sometimes, industries are located in or near the cities. Thus industrialization and urbanization go hand in hand. Cities provide markets and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc to the industry. Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. Gradually, a large industrial agglomeration takes place.
(A) Where were most of the pre-independence industrial units situated? 1
(B) How does a factory owner ensure the least cost of production? 1
(C) Name four factors of production. 2
SECTION – E
(Map Skill Based Questions)
[1 x 3 = 3]
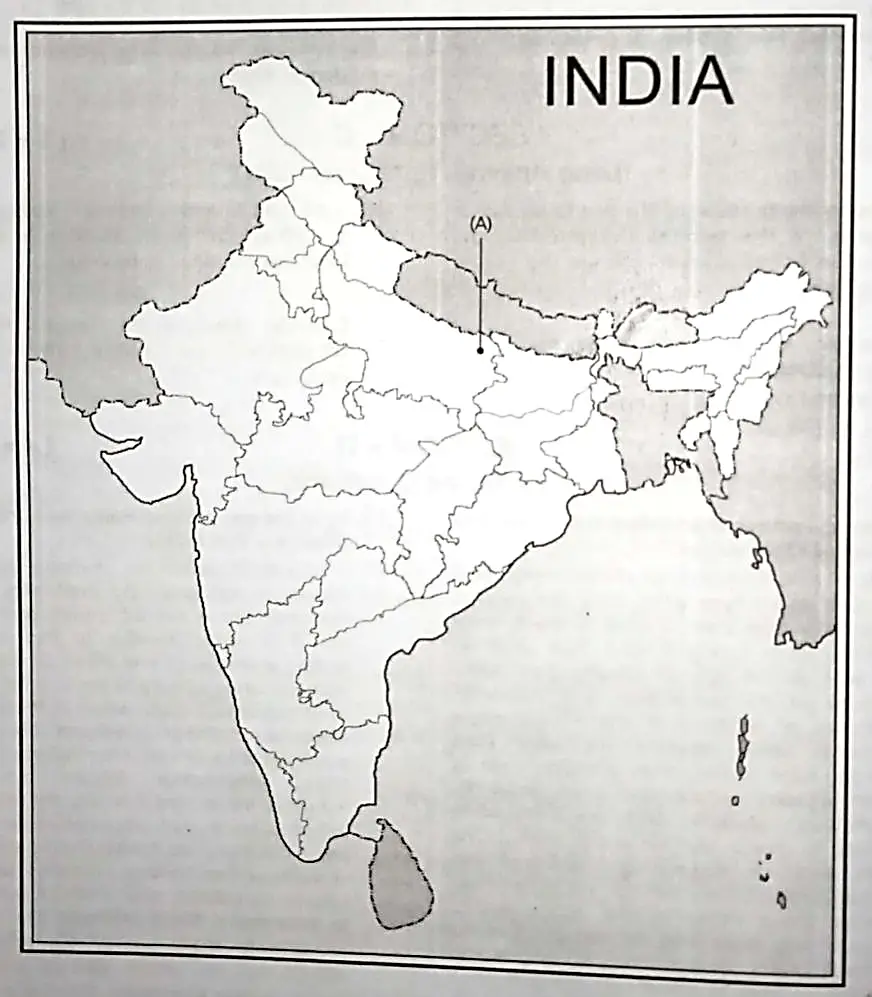
13. (A) On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(a) Identify the place associated with calling off the Non-Cooperation Movement. 1
(B) On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(a) Paradip Port
OR
Gandhinagar Software Technology Park 1
(b) Bhilai Iron and Steel Plant 1