| Textbook | NCERT |
| Board | CBSE Board, UP board, JAC board, HBSE Board, Bihar Board, PSEB board, RBSE Board, UBSE Board |
| Class | 6th Class |
| Subject | GEOGRAPHY | Social Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 |
| Chapter Name | Major Landforms of the Earth |
| Topic | Major Landforms of the Earth CBSE Class 6 GEOGRAPHY Chapter 6 Notes |
| Medium | English |
| Especially Designed Notes for | CBSE, ICSE, IAS, NET, NRA, UPSC, SSC, NDA, All Govt. Exam |
Major Landforms of the Earth
- Surface of the earth is not same everywhere.
- Some parts of the lithosphere may be rugged or some flat.
- In the ground of the earth, a slow continuous movement is going on.
- This continuous movement results in the formation of different types of landforms.
Land Forms
The landforms are a result of two processes:
- Internal process These processes generate in the interior of the earth and cause change in the surface of the earth.
- External process These processes generate by the external agents like-air and water and cause change in the surface of the earth.
Hill is a land surface higher than surrounding area. A steep hill with an elevation of more than 600 metres is termed as a mountain.
- The wearing away of the earth’s surface is called erosion in which the surface is being lowered, while the process of rebuilt is called deposition.
- These two processes are carried away by different agents, like- running water, ice and wind.
Types of Landforms
On the basis of elevation and slope, the landforms can be grouped into mountains, plateaus and plains.
Mountains
- A mountain is a natural elevation of the earth’s surface.
- Some mountains may have a small summit and a broad base and some are higher than clouds.
Glaciers
- The permanently frozen rivers of ice found in some mountains are called glaciers.
- Some mountains are also found under the sea.
Range
- Sometimes mountains arrange in a line called range.
- Various mountain systems having a series of parallel ranges widening over hundreds of kilometres.
- The Alps, the Andes and the Himalayas are mountain ranges of Europe, South America and Asia, respectively.
- Mountains vary in their heights and shapes.
Types of Mountain
Mountains are of three types:
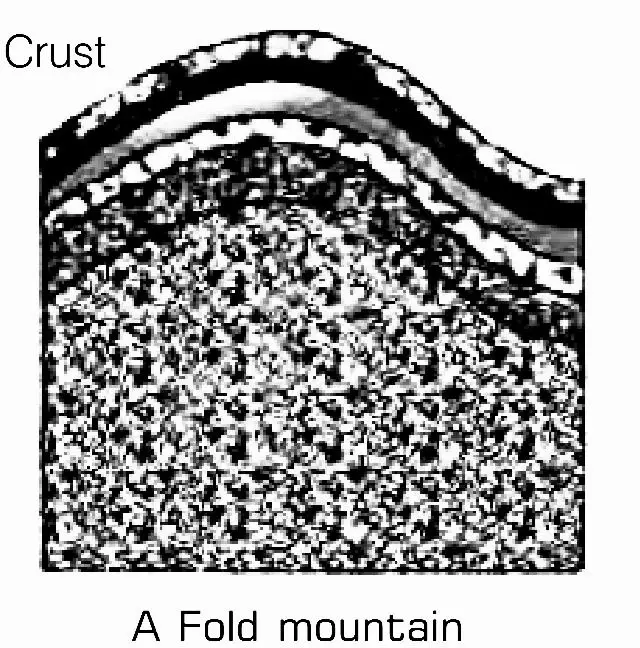
(1) Fold Mountain
- Fold mountains are with rugged relief and high conical peaks.
- For example- Himalayan mountains and Alps, while others with rounded features and low elevation like-Ural mountains in Russia and the Appalachians in North America.
- They are very old fold mountains.
- One of the world’s oldest fold mountain systems is the Aravali range in India.
- This range has considerably worn down due to the processes of erosion.
(2) Block Mountain
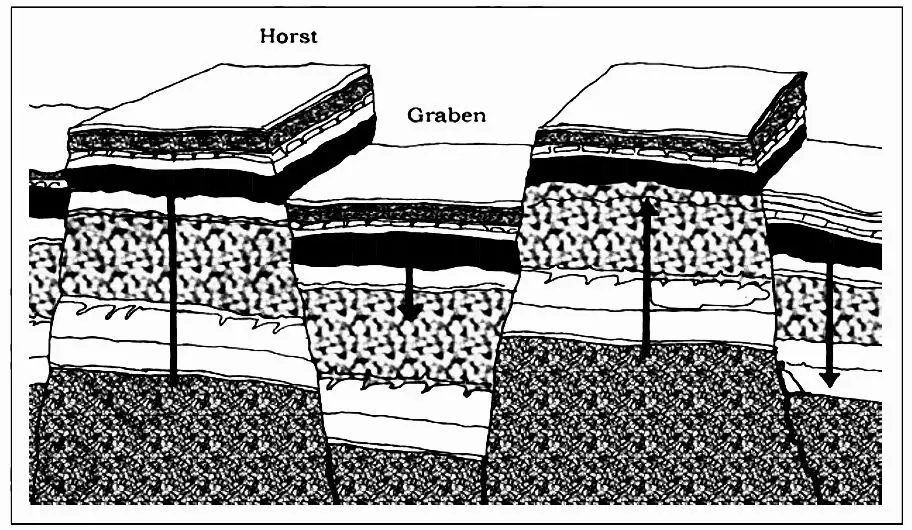
- Block mountains are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically.
- The uplifted blocks are termed as horsts and the lower blocks are called graben.
- The Vosges mountain and Rhine valley in Europe are examples of block mountains.
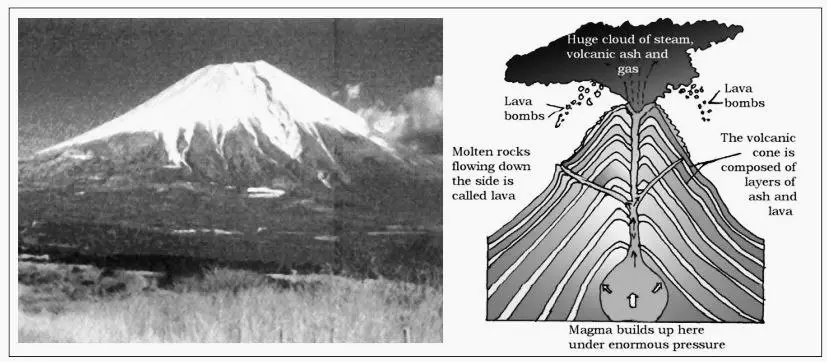
(3) Volcanic Mountain
- Volcanic mountains are formed by volcanic activities.
- They are formed by the deposition and solidification of lava.
- Mt. Kilimanjaro in Africa and Mt. Fujiyama in Japan are examples of such mountains.
Advantages of Mountain
The advantages of mountains are as follows:
- The river valleys and terraces are ideal for cultivation of crops. Mountains possess a rich variety of flora and fauna.
- Mountains have the rich forests cover which provide fuel, fodder, shelter and other products like gum, raisins, etc.
- Mountains attract a number of tourists and hence promote tourism. They visit mountains for their scenic beauty. Various sports like paragliding, hand gliding, river rafting and skiing are popular in the mountains.
Plateaus
- A plateau is an elevated flat land.
- A plateau may have one or more sides with steep slopes.
- It is a flat-topped table land standing above the surrounding area.
- The East African plateau in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda and the Western plateau of Australia are other examples.
- Plateaus may be young or old, the Deccan plateau of India is one of the oldest plateaus.
- The height of plateaus varies from few hundred metres to several thousand metres.
- The Tibet plateau is the highest plateau in the world with the height of 4,000 to 6,000 metres above the mean sea level.
Advantages of Plateaus
The advantages of plateaus are as follows:
- Plateaus are very rich in mineral deposit, this is the reason behind the locations of many mining areas in plateau regions in the world.
- The African plateau is famous for gold and diamond mining while Chhotanagpur plateau in India is famous for the deposition of manganese, coal and iron.
- In the plateau regions, several waterfalls are found as many rivers in India fall from a great height.
- The Hundru falls in the Chhotanagpur plateau on the river Subarnarekha and the Jog falls in Karnataka are examples of such waterfalls.
- The lava plateaus are rich in black soil that are fertile and good for cultivation.
Plains
- Plains are large areas or stretches of flat land.
- Generally, they are with the height of not more than 200 metres above mean sea level.
- Some plains are extremely level and some are with slightly rolling and undulating surface.
Formation of Plains
- Most of the plains are formed by the deposition of rivers and their tributaries.
- Plains generally are very fertile thus having thick population.
- Some of the largest plains made by the rivers are found in Asia and North America. For example:
- Asia continent, these plains are formed by the Ganga and Brahmaputra in India
- The Yangtze in China; the rivers flow down the slopes of mountains and erode them.
- They carry forward the eroded material. Then, they deposit their load consisting of stones, sand and silt along their courses and in their valleys. It is from these deposits that plains are formed.
Advantages of Plains
The advantages of plains are as follows:
- The plains are the most useful regions for the human habitation.
- The large flat areas are available for construction of houses, and productive for cultivation.
- The construction of transport network is easy in these areas because of plain surface.
Landforms and the People
- Human beings are living on different kinds of landforms in different ways.
- Leading a life is much tougher in mountain regions than plains.
- We can easily grow crops, build houses or a road in the plains than the mountains.
- Sometimes, natural calamities like earthquake, volcanic eruption, storms and floods cause widespread destruction and huge loss of life and property.
- But through awareness programmes about such incidents we may lower the risks.
- Usually, we use the land in a wasteful manner, For example constructing houses on a fertile land.
- Likewise we throw garbage on land or in water making them polluted.
One word meaning
- Hill It is a land surface higher than surrounding area.
- Erosion The wearing away of the earth’s surface is called erosion.
- Deposition The process of rebuilding earth’s surface is called deposition.